









Intelligent IoT Grids
Made Easy for You











IoT SMART GRID
MANAGEMENT
•
VIEW & CONTROL YOUR ASSETS OFF-SITE 24/7
•
THEFT & VANDALISM PREVENTION / DETECTION
•
REDUCE MAINTENANCE COSTS
•
INTERNET of THINGS TECHNOLOGY
•
SECURE CLOUD BASED SOFTWARE
•
LINK ALL YOUR ASSETS INTELLIGENTLY
•
MONITOR, CONTROL & DIAGNOSE ISSUES REMOTELY
•
REDUCE OPERATIONAL COSTS
•
ASSET & MAINTENANCE MANAGEMENT






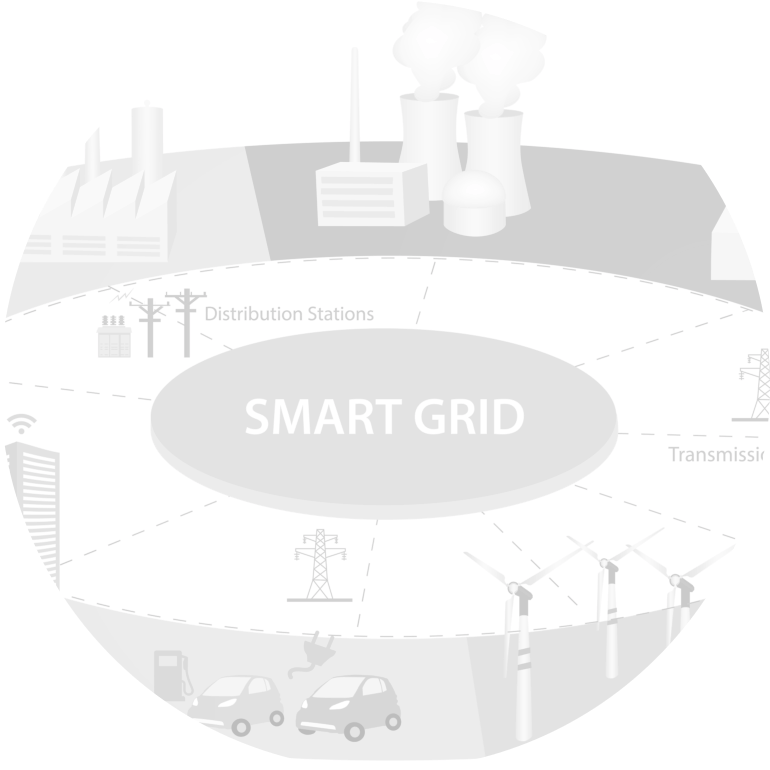
SMART GRIDS INTELLIGENTLY MONITORED, CONTROLLED, MANAGED & PROTECTED FROM ONE PLATFORM
SMART GRIDS IN A NUTSHELL:
•
Big
data,
advanced
analytics
and
IoT
technologies
(Internet
of
Things)
are
essential
technology
drivers
in
smart
grids
whereby
analytics
shift
to
the
edge,
as
in
edge
computing.
Smart
grids
leverage
more
technologies
with
an
obvious
key
role
for
IoT.
•
An
electrical
grid
is
a
network
to
deliver
electricity
from
the
producer(s)
and
places
where
it’s
generated
and
transformed
(power
plants
and
substations)
to
the
final
destinations
where
electricity
is
‘consumed’:
households,
businesses,
various
facilities and the consumer in general. In practice it is a highly interconnected network with several components such as substations, transmission lines and wiring, distribution lines, transformers and more.
•
The
purpose
of
a
n
electrical
grid
is
to
make
sure
that
electricity
is
always
provided
when
and
where
needed,
without
interruption
–
and
herein
lie
many
challenges
where
a
smart
grid
can
already
offer
solutions/answers
.
The
two-way
flow
of
electricity
and
data
that
is
the
essential
characteristic
of
a
smart
grid
enables
to
feed
information
and
data
to
the
various
stakeholders
in
the
electricity
market
which
can
be
analyzed
to
optimize
the
grid,
foresee
potential
issues,
react
faster
when
challenges
arise
and
build
new
capacities
–
and
services
–
as
the
power
landscape
is
changing.
The
electricity
market,
the
consumption
of
electricity,
regulations,
demands
of
various
stakeholders
and
the
very
production
of
electricity
are
all
changing. So, smart grid initiatives exist across the globe, with different approaches and goals.
•
However,
a
smart
grid
is
about
much
more
than
just
smart
metering
and
some
other
elements
include
the
distribution
lines
and
substations
(substation
automation
and,
increasingly,
digital
substations),
technologies
and
mechanisms
to
prevent
power
outages
and
ensure
power
quality
(availability,
reliability,
etc.),
the
integration
of
energy
from
various
sources
with
an
increased
focus
on
‘green
energy’,
smart
power
generation,
sensing
along
transmission
lines,
power
system
automation,,
the
inclusion
of
micro-generation
whereby
especially
organizations
and
larger
facilities
can
generate
their
own
power
and
supply
it
to
the
central
network
grid
(on
top
of
prosumers
-
people
that
both
produce
and
consume
power),
better
and
more
power storage capabilities, ways to enhance security, alternative transmission methods to save on precious metals and the design of more modern and stable electrical grids in countries and areas where old grids need replacement.
•
“One
of
the
primary
characteristics
of
a
smart
grid
is
its
ability
to
self-heal
with
flexibility
”.
Pointing
to
FLISR
technology
(fault
location,
isolation,
and
service
restoration)
self-healing
capabilities
minimize
blackouts
because
they
allow
for
continuous
self-assessments
that
inspect,
analyze,
react
to,
and
automatically
respond
to
problems.
This
is
made
possible
through
the
widespread
deployment
of
sensors
and
other
intelligent
devices
and
automated
controls
that
check
and
evaluate the status and condition of the network to identify abnormalities and problems.
•
In
short,
the
digital
technology
that
allows
for
two-way
communication
between
the
utility
and
its
customers,
and
the
sensing
along
the
transmission
lines
is
what
makes
the
grid
smart.
Like
the
Internet,
the
Smart
Grid
will
consist
of
controls,
computers, automation, and new technologies and equipment working together, but in this case, these technologies will work with the electrical grid to respond digitally to our quickly changing electric demand.
•
The benefits associated with the Smart Grid include:
o
More efficient transmission of electricity
o
Quicker restoration of electricity after power disturbances
o
Reduced operations and management costs for utilities, and ultimately lower power costs for consumers
o
Reduced peak demand, which will also help lower electricity rates
o
Increased integration of large-scale renewable energy systems
o
Better integration of customer-owner power generation systems, including renewable energy systems
o
Improved security & Management



















© 2016-2023 Intelligent IoT Solutions (Pty) Ltd.
Products
Enclosure Controllers
Light Controllers
Combo Sensors
Gateways
Conditions & Warranties
Company
Presentations
Brochures
Services
















IOT-SOLUTIONS

INTELLIGENT
















INTELLIGENT SMART GRIDS FOR A FUTURE READY CITY











REPORTS / LOGS



•
Auto Reports / Logs
o
Auto Maintenance / Repair Job Card
o
Communication Info (RF,)
o
Health Status
o
Alerts / Alarms
COMMUNICATION















SYSTEM SECURITY








































MONITORING
CONTROL

























ALARMS / ALERTS
!


!
•
Devices to Network Server
o
LTE / 4G (Back-fall) directly via public
mobile network
o
Ethernet directly via Fibre Network if
available
•
Devices & Server
o
Fibre / Ethernet (Primary )
o
LTE / 4G (Back-fall) directly via
public mobile network
•
Network / Application Server
o
Secure
Embedded
end-to-end
encryption
128
AES
(Advanced
Encryption Standard)
•
User Level of Authority
o
4 User Level of Authority as default
o
Can be modified as per client request
o
User login name & password required
o
Access Time period restriction

•
Controllers (Light + Access) Status
o
Mains Power
o
Phase Monitoring
o
Battery Back-up
o
Operational Temperature
o
Communication (RF)
o
See Smart Light Monitoring
•
Access Entrance Status
o
Authorised Entry
o
Unauthorised Entry (Forced Entry)
•
Alarm / Alert Status
o
Power Failure, Comms. Failure etc.
o
Attempted Theft / Tampering
o
Abnormal Movement / Vibrations
•
Output Control
o
12VDC Output for Solenoids
o
12VDC Output for Motors
•
Input Control
o
Door Sensors
o
Vibration Sensors
o
Temperature Sensors
•
Light Control
o
See Smart Light Control

•
Controllers (Lights + Access)
o
Communication Issue Alert
o
Battery Back-up Alarm / Alert
o
Power Failure Alarm / Alert
o
Temperature Alarm / Alert
o
Cable theft / Tampering Alarm
o
Accelerometer Sensor Alarm / Alert
•
Light Alarms / Alerts
o
LED Driver Alerts
o
Light not Functioning
o
Power Failure Alarm / Alert
o
Temperature Alarm / Alert
o
Light Fitting & Pole Tampering Alarm